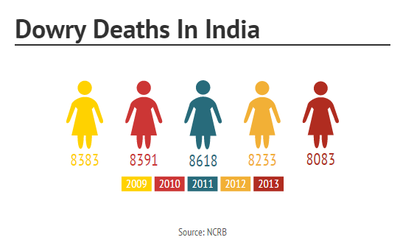
The Dowry Prohibition Act goes some way to diminish the oppression and fatalities surrounding dowries in India. However recent Dara shows this terrible scourge is still very much extant. According to Statistica in 2016, there were 7621 dowry deaths across the nation.
Dowry deaths refers to the bride’s suicide or murder committed by her husband or his family soon after the marriage due to discontent with the amount of the dowry paid.
What is the Dowry Prohibition Act about?
- The Dowry Prohibition Act, 1961 prohibits the practice of giving or taking of a dowry by either parties to a marriage. The law also punishes the demanding and advertising of a dowry.
- It imposes a duty on parties getting married to make a list of gifts and presents.
- If a dowry has been exchanged at a wedding then the law imposes a duty on the person who is giving the dowry to give it to the bride.
- It should be noted that the more serious crimes in relation to dowries including dowry death and cruelty from dowry demands are punishable under the general law on crimes – the Indian Penal Code, 1860.
Who can be punished under this Act?
- Any person who gives or takes a dowry (minimum punishment of five years);
- Any person who helps someone to give or take a dowry;
- Anyone who in any way demands a dowry;
- Anyone who advertises and offers to give money or property in return for marrying his son, daughter or relative;
- Anyone who publishes these advertisements;
- Anyone who does not hand over the dowry to the bride within the specified time.